|
Saeed Iqbal I have been awarded Ph.D. by the Department of Computer Science at the University of Central Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan, in May 2023. During my doctoral research, I focused on analyzing medical images from various modalities using cognitive poly-representation of data, machine learning, and image processing techniques. With a Master of Science degree from the National University of Computer & Emerging Sciences, Pakistan, my research combines both medical and computational aspects to enhance the diagnosis and prognosis in healthcare patients. Presently, I hold the position of Assistant Professor of Computer Science within the Faculty of IT&CS at UCP. I take pride in the successful planning, organization, and implementation of two undergraduate programs, namely Data Science and AI, as well as a postgraduate program, MSDS, in the Department during the Fall of 2021. With over a decade of experience in administration, I have garnered recognition at various forums for my commendable efforts in facilitating steady and sustainable growth, aligning with the University's vision and mission. Furthermore, I am a member of the Healthcare Modeling and Informatics group within the Centre for Applied Data Analytics. This group is dedicated to fostering collaborations with clinicians and researchers from national hospitals, aiming to develop solutions for automated analysis and prediction of disease prevalence and progression in both cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. Email / Resume / Google Scholar / Linkedin / Github |
|
ResearchMy research focuses on computer-aided analysis of medical images from various modalities, resulting in multiple publications in esteemed journals and conferences. Notable contributions include addressing challenges in melanoma classification, chest X-Ray classification, lung cancer nodule detection, CT analysis of traumatic brain injury (TBI) cases, Barret’s Esophagus classification, retinopathy classification, and automated segmentation of space-occupying lesions. |
|
|
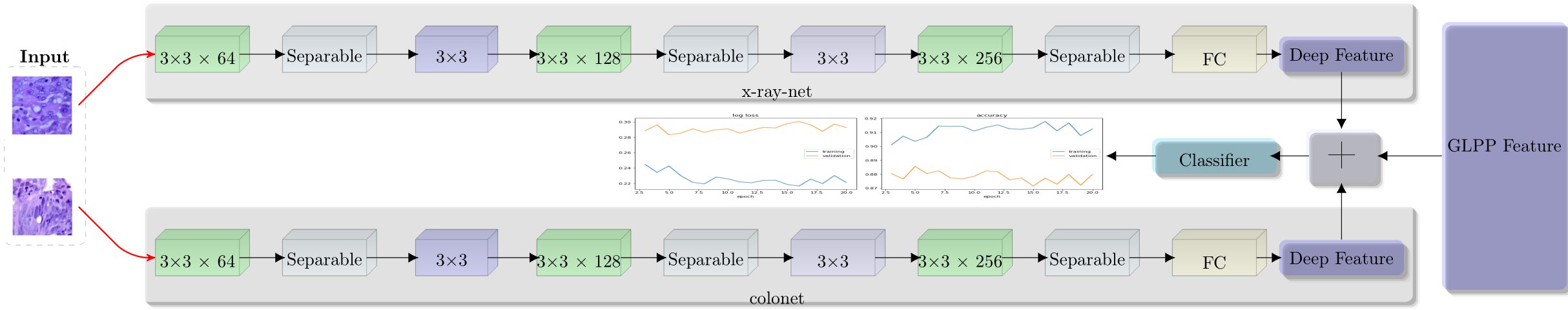
Fusion of Textural and Visual Information for Medical Image Modality Retrieval using Deep Learning-Based Feature Engineering
Saeed Iqbal, Adnan N. Qureshi, Musaed Alhussein , Imran Arshad Choudhry, Khursheed Aurangzeb, Tariq M. Khan IEEE ACCESS, MDPI, 2023 Impact Factor: 3.9, HEC-Category:W, Manuscript direct Link / DOI This study introduces an innovative approach to medical image retrieval that combines textural and visual information. The goal is to assist healthcare professionals in accurately selecting the imaging modality. Deep learning-based feature engineering is employed to extract textural and visual components from medical images, enhancing discrimination capabilities. The method outperforms conventional techniques in modality retrieval, achieving a precision of 95.89 and a recall of 96.31 in evaluations. By integrating textural and visual data, this approach improves classification accuracy and robustness, offering a valuable tool for enhancing medical image processing and diagnosis. |
|
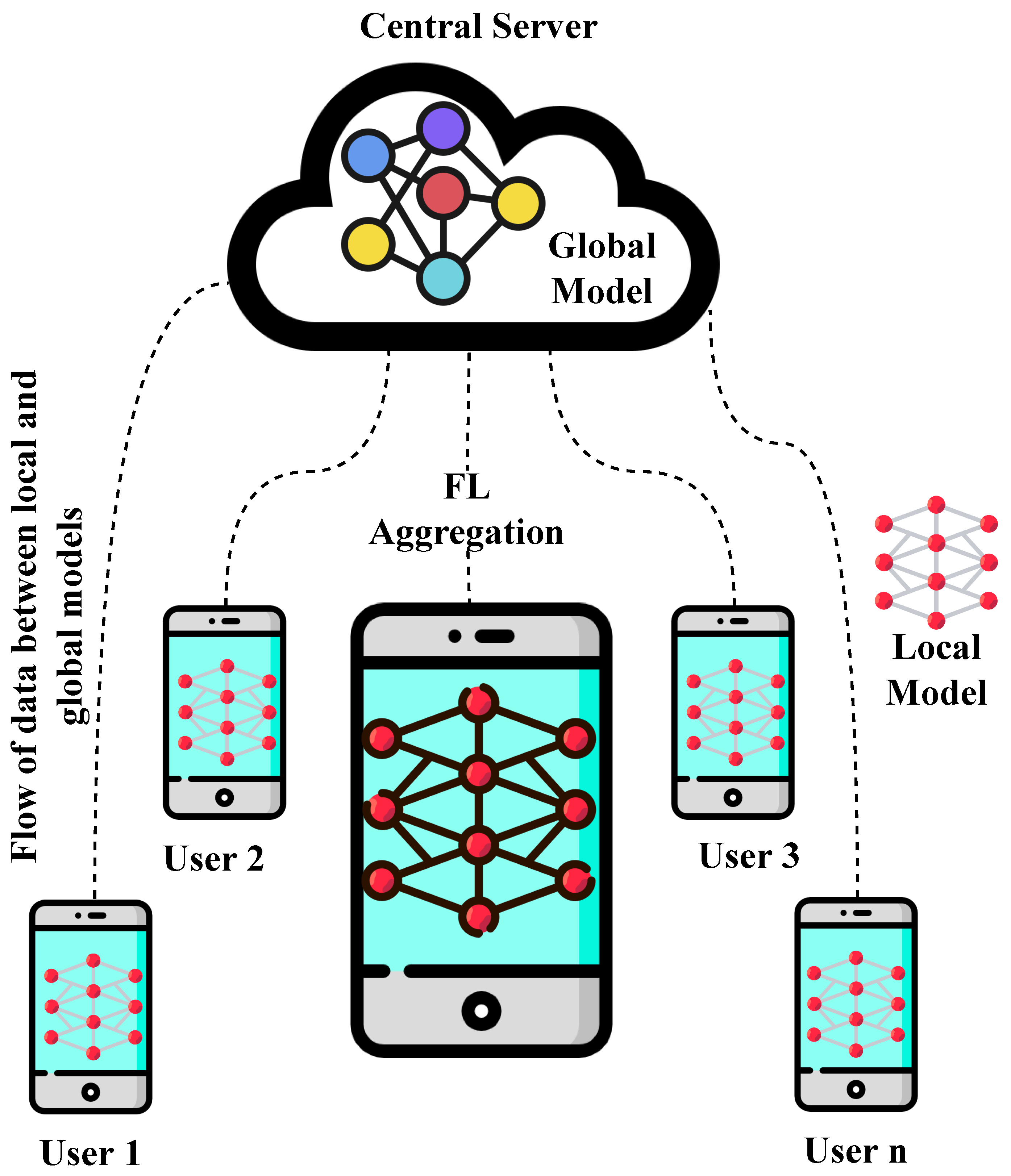
A Novel Heteromorphous Convolutional Neural Network for Automated Assessment of Tumors in Colon and Lung Histopathology Images
Saeed Iqbal, Adnan N. Qureshi, Musaed Alhussein , Khursheed Aurangzeb, Seifedine Kadry Biomimetics, MDPI, 2023 Impact Factor: 4.5, HEC-Category:X, Manuscript direct Link / DOI This paper introduces "ColonNet," a novel approach for the accurate assessment of mitotic nuclei in colon and lung tumor images. These nuclei are crucial indicators of tumor aggressiveness. The model comprises two stages: identification of potential mitotic patches and their categorization into specific tumor types using deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). These networks are combined in a heteromorphous architecture, enabling the capture of diverse tumor characteristics. In comparison to existing CNN models, ColonNet demonstrates superior performance. It achieves remarkable metrics, including an F1 score of 0.96, sensitivity and specificity of 0.95, and an area under the accuracy curve of 0.95. These results highlight the model's precision in tumor assessment. The researchers envision ColonNet as a valuable tool to aid pathologists in diagnosing colon and lung tumors. |
|
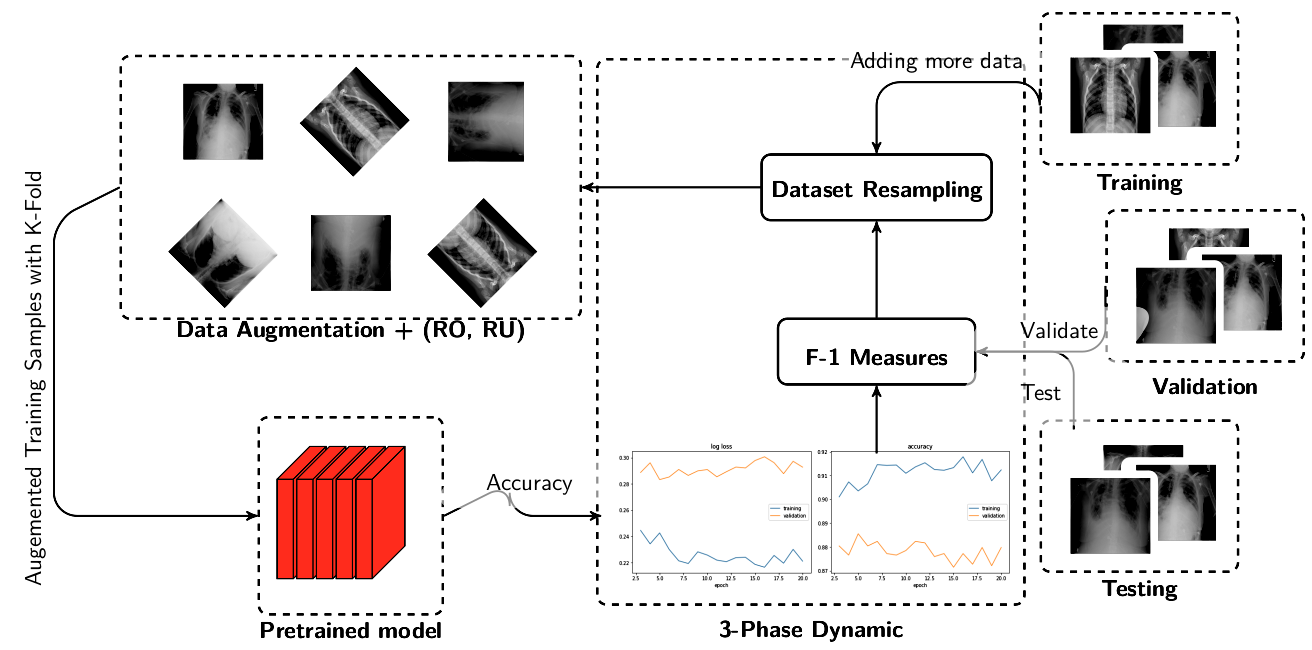
Privacy-Preserving Collaborative AI for Distributed Deep Learning
with Cross-sectional Data
Saeed Iqbal, Adnan N. Qureshi, Khursheed Aurangzeb, Khalid Javeed IEEE 5th International Conference on Bio-engineering for Smart Technologies (BioSMART), Paris, France, 2023 DOI The article tackles deep learning challenges in healthcare due to data limitations and privacy concerns. It concentrates on classifying intricate skin lesion images. Introducing "skin-net," a unique CNN model, it employs progressive private federated learning to address these issues. Recent advances in medical image analysis using CNNs and federated learning show promise (96.19 accuracy, 96.37 sensitivity, 96.53 specificity) in private skin disease classification. This method effectively evaluates human skin and bolsters model generalization via image augmentation. |
|
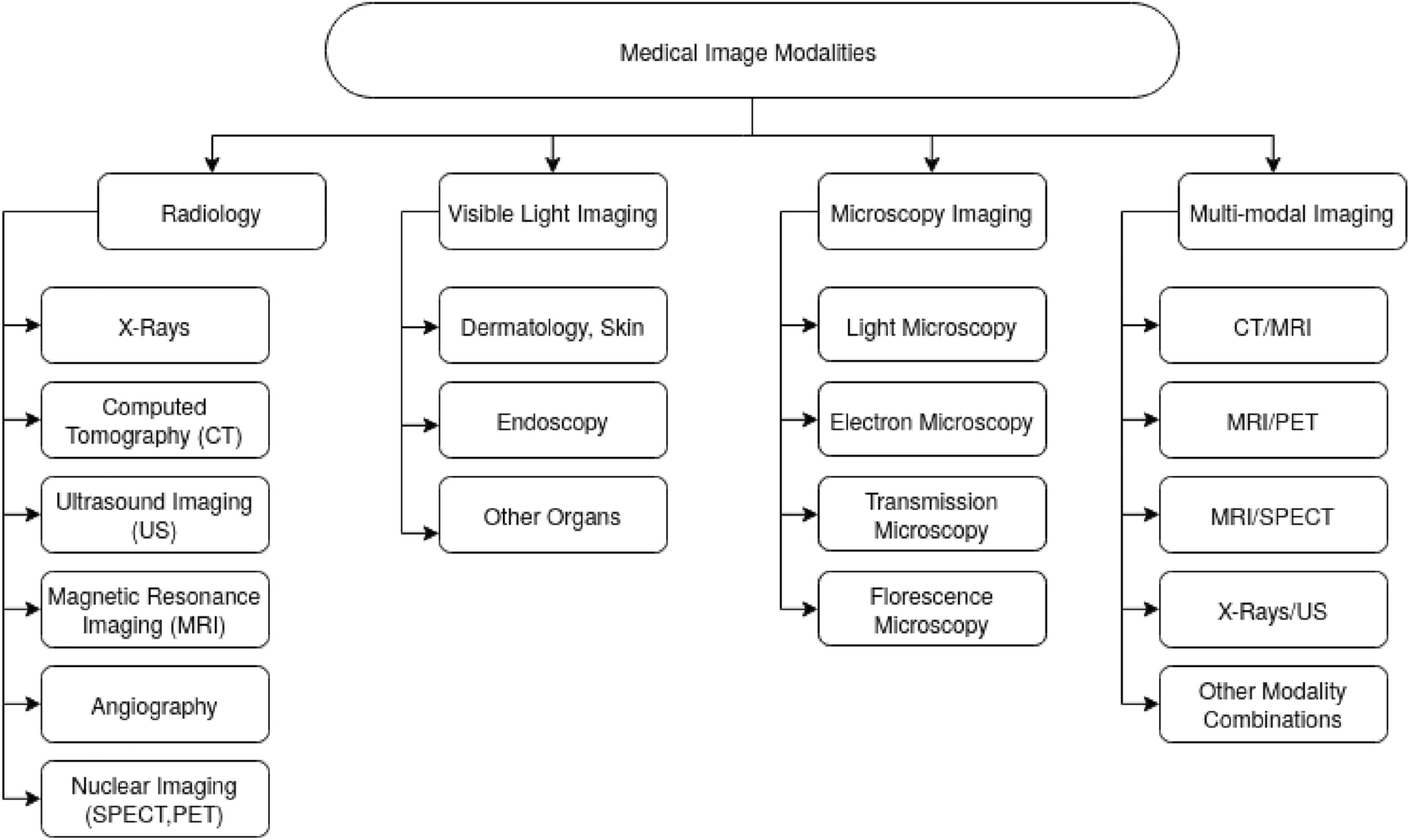
Dynamic learning for imbalanced data in learning chest X-ray and CT images
Saeed Iqbal, Adnan N. Qureshi, Jianqiang Li, Imran Arshad Choudhry, Tariq Mahmood Heliyon, Cell Press, 2023 Impact Factor: 3.776, HEC-Category:W, Manuscript direct Link / DOI In the context of limited data during novel research, we introduce a method to address imbalanced datasets in lung disease detection using X-ray and CT images. Our approach employs deep learning techniques to extract visual attributes, representing object features probabilistically. A minority class imbalance is managed with a sample analyzer, utilizing Support Vector Machine (SVM) for image classification. The proposed technique (3-Phase Dynamic Learning - 3PDL) and parallel CNN model (Hybrid Feature Fusion - HFF) achieve remarkable F1 score of 96.83 and precision of 96.87, making it a potential tool for pathologists. |
|
On the Analyses of Medical Images Using Traditional Machine Learning Techniques and Convolutional Neural Networks
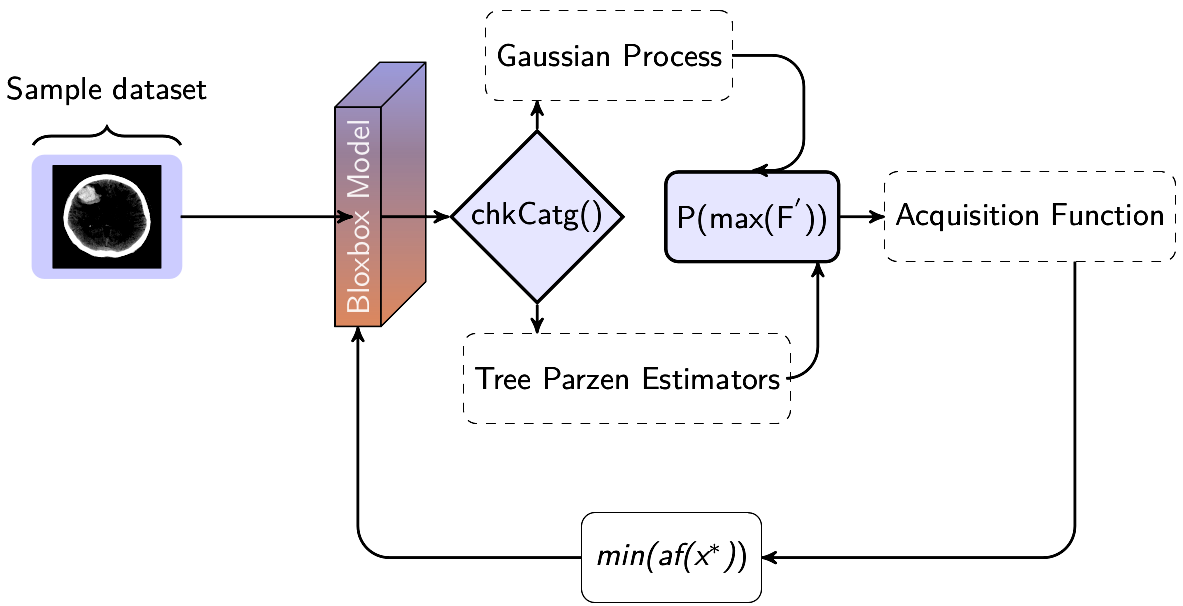
Saeed Iqbal, Adnan N. Qureshi, Jianqiang Li, Tariq Mahmood Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, Springer, 2023 Impact Factor: 8.171, HEC-Category: W Manuscript direct Link / DOI CNNs excel in Object Detection, Segmentation, 2D and 3D Reconstruction, and more. Their feature learning during data augmentation, combined with recent Deep Learning enhancements like activation functions and regularization, has elevated CNN's performance. Innovations in CNN architecture and representation have further amplified its effectiveness. This survey explores deep learning taxonomy, diverse CNN models, their depth, width, components, applications, and ongoing challenges. |
|
Improving the Robustness and Quality of Biomedical CNN Models through Adaptive Hyperparameter Tuning
Saeed Iqbal, Adnan N. Qureshi, Jianqiang Li, Amin Ullah, Tariq Mahmood Applied Sciences, MDPI , 2022 Impact Factor: 2.838, HEC-Category: W Manuscript direct Link / DOI Deep learning's potential in disease detection and medical image analysis is widely acknowledged, but optimal hyperparameter selection often affects algorithm performance. To address this, we introduce Adaptive Hyperparameter Tuning (AHT) for Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) training. AHT empowers CNN models to autonomously select optimal hyperparameters for medical image classification. Our CNN model, Deep-Hist, achieves 95.71% accuracy in categorizing medical images as malignant or benign. With its strong F1 score, precision, generalization, and accuracy, the model holds promise as a valuable tool for pathologists. |
|
|
A Heteromorphous Deep CNN Framework for Medical Image Segmentation Using Local Binary Pattern
Saeed Iqbal, Adnan N. Qureshi IEEE Access, IEEE 2022 Impact Factor: 3.367, HEC-Category: W Manuscript direct Link / DOI Detecting mitotic nuclei in breast cancer samples aids in tumor aggressiveness assessment. Automating this is complex due to their resemblance to non-mitotic nuclei. The study introduces BreastUNet, a novel heteromorphous Deep Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) with feature grafting for mitotic nuclei analysis. It identifies potential mitotic patches and classifies them, outperforming state-of-the-art CNNs with an F1 score of 0.95, Sensitivity/Specificity of 0.95, and area under the precision curve of 0.95. The model's strong performance suggests its potential as a tool for pathologists. |
|
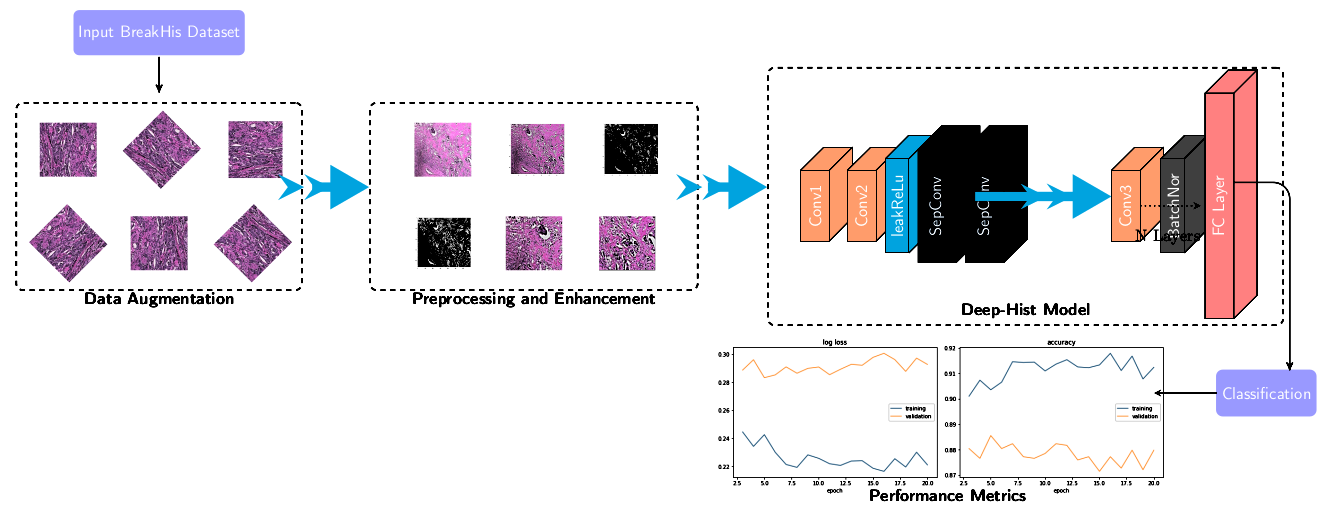
Deep-Hist: Breast cancer diagnosis through histopathological images using convolution neural network
Saeed Iqbal, Adnan N. Qureshi Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, IOS Press, 2022. Impact Factor: 1.739,HEC-Category: X Manuscript direct Link / DOI Histopathological images are crucial for breast cancer diagnosis, demanding meticulous microscopic analysis. However, this process is time-consuming, susceptible to human error, and requires expertise in various magnifications. Conventionally, data labeling assumes uniform labels for all patients due to labeling complexity. This study explores machine learning's value in histopathological breast cancer diagnosis, using the BreakHis dataset. Our "Deep-Hist" model achieves >92.46% accuracy with Stochastic Gradient Descent, making it useful for research and clinical second opinions.. |
|
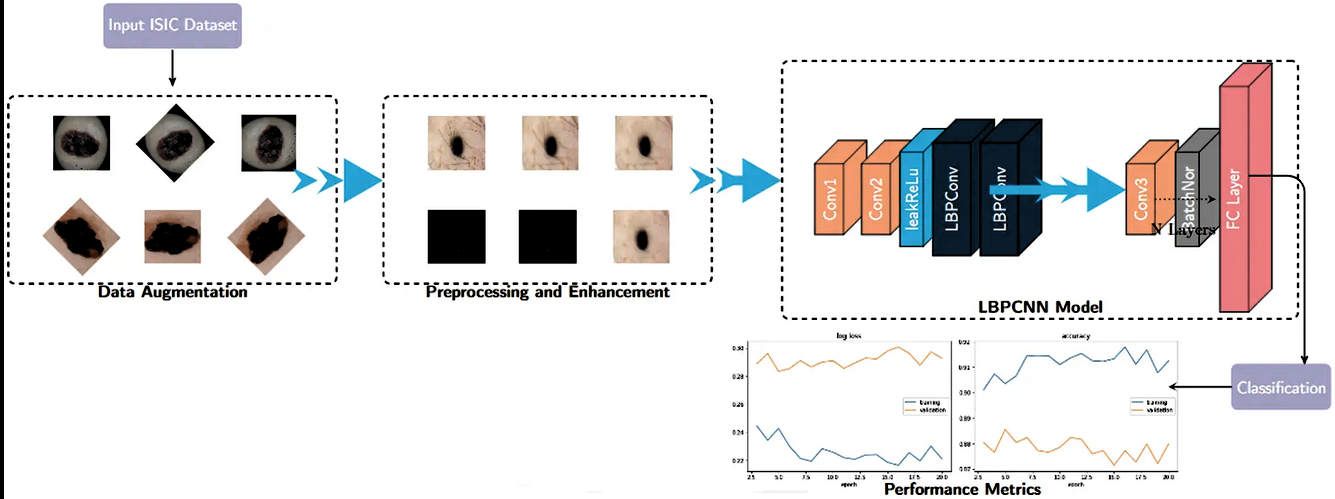
Hybridization of CNN with LBP for Classification of Melanoma Images
Saeed Iqbal, Adnan N. Qureshi, Ghulam Mustafa Computers, Materials & Continua (CMC), Tech Science Press,, 2022 Impact Factor: 3.860, HEC-Category: W Manuscript direct Link / DOI Skin cancer (melanoma) is highly aggressive, driven by increased UV exposure. Timely lesion detection is vital for improved lifestyle and reduced mortality. We've developed a hybrid approach combining convolutional neural networks (CNN) and local binary patterns (LBP) for lesion analysis. Evaluating on ISIC datasets (2017, 2018, 2019) with augmented data, our novel CNN-LBP architecture achieves 97.29% accuracy, 95.63% sensitivity, and 97.90% specificity for classifying skin cancers. This approach holds promise for research and clinical second opinions, closely aligning with expert intuition. |
|
|
Data Mining of Scientometrics for Classifying Science Journals
Muhammad Shaheen, Ali Ahsan, Saeed Iqbal Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing (IASC), Tech Science Press, 2021 Impact Factor: 1.647, HEC-Category: W Manuscript direct Link / DOI Validating scientific work through various Scientometrics is a concern due to their suitability and validity. To address this, a unified journal ranking system is proposed, collecting and assessing data via data mining. Utilizing K Means clustering and Naïve Bayes classification, the approach achieves 80% accuracy, introducing metrics like Eigen factor, Audience Factor, Impact Factor, Article Influence, Citations, and Prestige of Journal (PoJ). This adaptable method can be applied beyond journal classification. |
|
|
Using Local Binary Patterns and Convolutional Neural Networks for Melanoma Detection
Saeed Iqbal, Adnan N. Qureshi, Mukti Akter Book Series Proceedings of SAI Intelligent Systems Conference, Intelligent Systems and Applications (IntelliSys), Springer Link, 2019 Manuscript direct Link / DOI Skin cancer arises from abnormal skin cell growth in sun-exposed areas. Early detection is crucial, but manual assessment of medical cells and images is laborious and subjective. This paper introduces a new method utilizing segmentation and region analysis to detect skin cancer signs like asymmetry, border, color, and diameter. Employing Local Binary Pattern Convolutional Neural Networks achieves high performance with 0.95 accuracy, 0.95 sensitivity, and 0.96 specificity on ISIC datasets. |
|
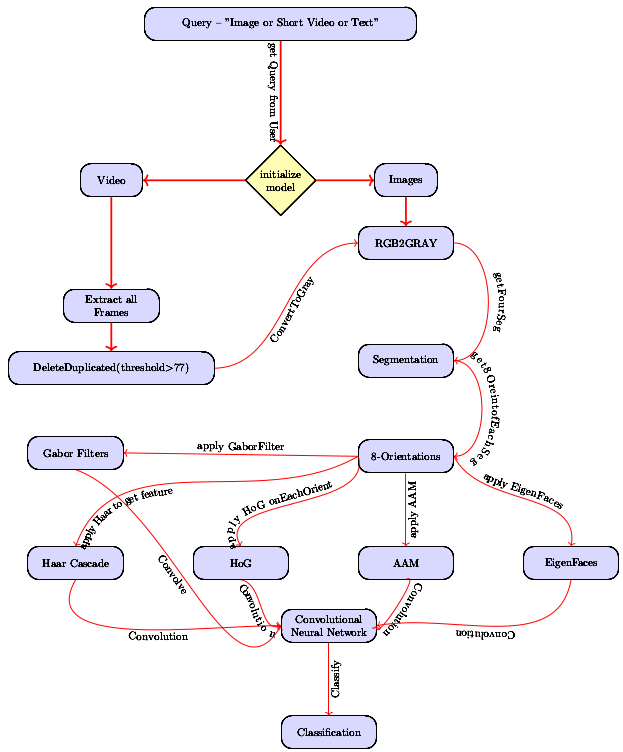
Content Based Video Retrieval Using Convolutional Neural Network
Saeed Iqbal, Adnan N. Qureshi, Awais M. Lodhi Book Series Proceedings of SAI Intelligent Systems Conference, Intelligent Systems and Applications (IntelliSys), Springer Link, 2018 Manuscript direct Link / DOI We present a content-based retrieval method for unconstrained videos, focusing on object detection and classification. Videos are segmented to identify human-defined objects of interest, utilizing algorithms like Haar-cascade, Gabor filter, AAM, and CNN for localization and intensity measurement. Employing Youtube and SegTek datasets with 2000+ videos, cluster computing ensures advanced results for object detection and segmentation. |
|
|
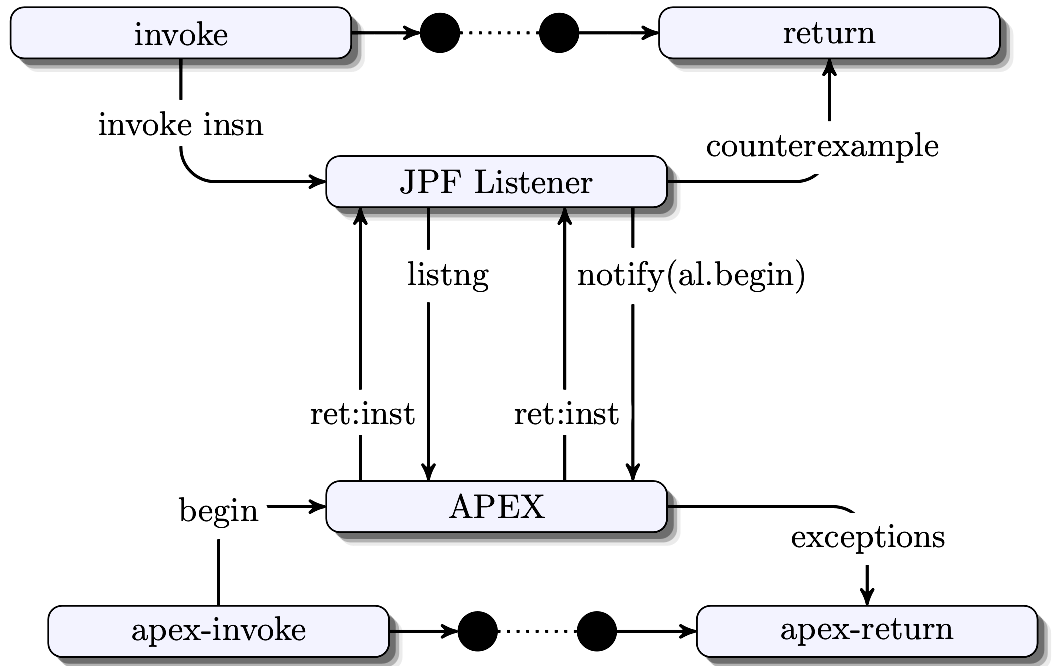
Verification of Android Permission Extension Framework using SPF and JPF
Saeed Iqbal, Imran Arshad Choudhry, Kamran Shabbir International Journal of Computer Science and Information Security, 2016 Model checking is a formal verification method exploring diverse paths with varied runtime inputs. Symbolic Pathfinder, a recognized approach, employs symbolic values for System Under Test (SUT) inputs, executing SUT by manipulating expressions. This paper introduces symbolic execution for the Android Permission Extension (APEX) framework, permitting permission changes at runtime. Using Symbolic Pathfinder (SPF), a prominent tool, APEX verification identifies a race condition and compares performance with other tools. |
|
|
A machine learning based method for optimal journal classification
Saeed Iqbal, Muhammad Shaheen, Fazl-e-basit 8th International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions (ICITST-2013), IEEE, 2013 Manuscript direct Link / DOI We conduct a thorough examination of bibliometric indicators for journal performance, including Eigenfactor, Impact Factor, Audience Factor, and Article Influence Weight. We aim to identify previously overlooked parameters and limitations in existing algorithms. Our goal is to introduce a new journal performance factor for more effective ranking. Leveraging Bayesian classification, a prevalent machine learning technique, we classify journals using our approach and compare outcomes with prior methods. |
|
< |
Labeled clustering a unique method to label unsupervised classes
Muhammad Shaheen, Saeed Iqbal, Fazl-e-basit 8th International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions (ICITST-2013), IEEE, 2013 Manuscript direct Link / DOI This paper introduces a method to label unsupervised classes using clustering techniques. Specifically, K-Means clustering groups data based on similarity measures. We propose a unique approach involving correlation analysis and frequent membership function to label these classes. Applied to a world energy dataset, the method divides nations into labeled clusters, aiding energy sector decision-making. While minor deviations from real energy scenarios occur, the approach enhances data insights. |
|
Extending Java Pathfinder (JPF) with property classes for verification of Android permission extension framework
Saeed Iqbal, Shakir Ullah Shah, Mohammad Nauman, Muhammad Amin 2013 IEEE 3rd International Conference on System Engineering and Technology, IEEE, 2013. Manuscript direct Link / DOI This paper proposes a dynamic verification technique for the APEX framework, which allows runtime permission changes. Employing model checking, it ensures comprehensive understanding by exploring diverse paths with abundant inputs. Java Pathfinder (JPF) is used to verify APEX, revealing a key finding – the identification of a race condition within the framework. |